Having a brilliant idea that you can turn into a product or a service attractive for customers, helping your company grow just like in fairytales – that’s a dream scenario, which can fall apart just as quickly as it started.
If in the previous article I tackled the methods you can use to generate traction for your startup, now I will explain where and why some businesses end up failing right at the beginning of their road.
The problems that startups face on a global scale – what the studies say
According to a study published on entrepreneur.com, the most common problem that most start-ups encounter is related to cash flow – 82%. The next reason – 42% – is that there is no market interest for the products / services offered. Then, 29% of businesses run out of money, 23% do not have the right team, and 19% are overtaken by competitors.
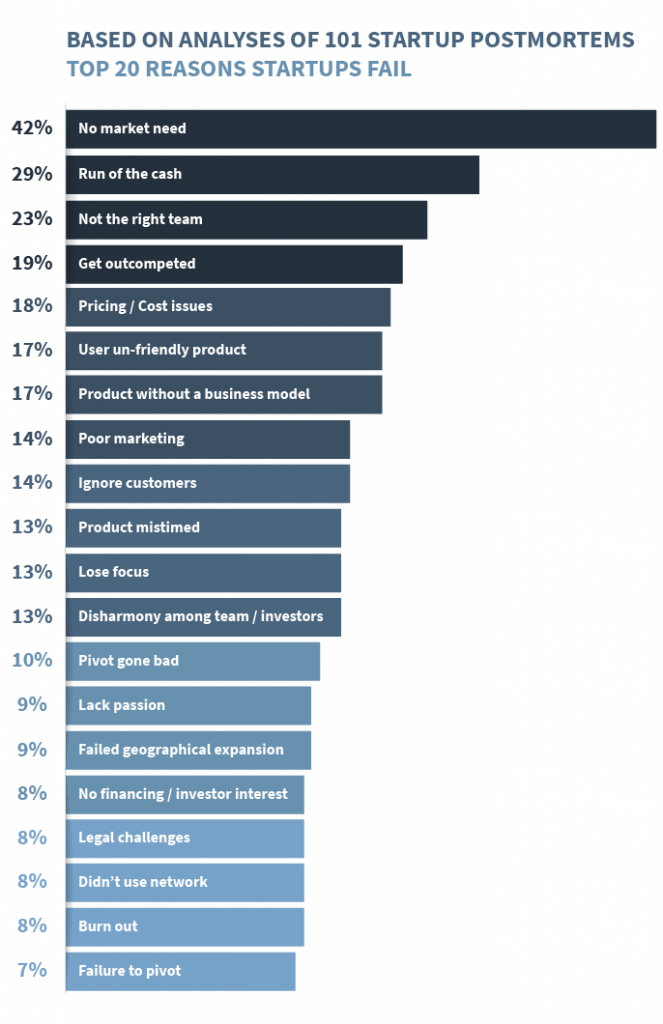
Another research paper, this time published by CB Insights, lists 20 of the most common reasons why startups fail. Unsurprisingly, 42% of the analyzed companies failed because they promoted goods and services for which there was no real need in the market. 29% of businesses ran out of funds, and 23% said the lack of a suitable team was the main reason for their collapse.
Here is the full graph below:
What other factors can cause a startup to crash?

Ranjay Gulati, professor of business administration at Harvard Business School, identified other elements that can lead to the failure of a startup. These are some of the reasons he established:
• Fear of fixed structures and hierarchies: When a business is in its infancy, the entrepreneurial spirit can run freely, but when the business starts to scale up, certain fixed structures, hierarchies and rules are required. These will help you better manage unforeseen situations and create a safer environment for employees.
• Copying other business models: If your startup loses the elements that set it apart from the competition and make it unique, then the chances of success fall dramatically.
• Inappropriate organizational culture: People are the most important asset of a company, and if you fail to align the company’s vision with their personal vision and values, then you will have a soulless business, doomed to fail.
• Talent (or lack of it): Sometimes you need talented people in key positions. Are you ready to find and recruit them? If so, then you have something major to gain. If not, then you have a lot to lose.
• You fail to keep your core business afloat and, at the same time, to find new growth opportunities: the solution to keep going would be to never forget where you started your business from and what is your main goal.
In “Why Startups Fail: A New Roadmap for Entrepreneurial Success,” another Harvard professor, Tom Eisenmann, explains the 11 steps that he identified by studying the quick ascension of some startups.
According to Eisenmann, these are:
• identifying an opportunity;
• a spectacular growth from the very beginning, driven by the first customers’ enthusiasm, the so-called early adopters;
• achieving success in generating capital, as investors bet on a good idea and a vision they relate to;
• then the rivals enter the scene – whether they are just copycats or giants in the industry interested only in counterattacking, they can still sell cheaper or invest more in marketing;
• the market becomes oversaturated, finding itself in a desperate need for a major investment in marketing and promotion, also increasing costs;
• the team expands and problems with customers start to appear, as new employees do not have the training and the time needed to adapt to organizational values and the company’s workflow;
• the dire need for new specialists and systems arises, but coordinating a large and diverse team requires certain skills, as well as time to develop them;
• internal conflicts begin to emerge, and high-level decisions are taken with increased difficulty;
• there are problems related to ethics, which can also affect employees;
• investors begin to doubt the profitability of the respective business;
• the company collapses under all this pressure.
Why do Romanian startups fail?

According to the EY 2019 Barometer, the main obstacle in Romania for entrepreneurs launching a business is the mentality and fear of failure (20%), and poor education (13%). According to the same study, one out of two “Romanian start-ups has been on the market for less than 12 months”, and “about a third of start-ups fail to reach their second year”.
Moreover, the proportion of companies with a longer lifespan (2-3 years) decreased to 21% in 2019 from 26% in 2017, after a significant advance of 9% compared to 2016.
“The perception regarding the regulatory and fiscal environment may be one of the causes for the low survival rate of startup businesses”, is another important conclusion of the barometer.
The reasons why Romanian startups fail – in close connection with the fiscal and political environment.

Although the survey’s results list the “mentality and fear of failure” as the biggest obstacles to growing a business in Romania (20% of responses), the other factors have a significant importance because they fuel the entrepreneurs’ fear of this anxiety.
Fiscal unpredictability, high taxes and the “current political situation” are far from encouraging businessmen to overcome their problem, although the survey, which asked them to choose a single obstacle, shows smaller proportions of answers for the three options above: 12%, 9% and 12% respectively.
The lack of development funds (10%), access to finance (7%), and excessive bureaucracy (7%) are also hindering the success of startups.
Financing
Only 16% of the participants indicated the non-reimbursable financing from the Romanian government as the source used to the greatest extent, so that the importance of this factor remains only statistical when compared to 2017 (4%).
Most of the financing is through own funds (savings, personal loans, salaries – 79%) and by help from family and friends (14%).
Sponsorships are more important than bank loans for start-ups (4% compared to 3%). Likewise, grants, crowdfunding, supplier credit, and others have a bigger importance (5%). Also, the angel investors’ contribution is five times higher than it was in 2017.
“The situation may change in the country, but this change may materialize in the long run, because it will take some time for foreign investors to come to Romania in greater numbers,” the EY study concludes.
Conclusion
As we have seen, plenty of obstacles can arise in the way of a startup looking for its breakthrough. However, the success or failure of businesses depends largely on the involvement, passion, and determination of the entrepreneur.
If he has all the above-mentioned qualities, he will certainly not forget about the initial feasibility studies, he will not neglect his financial management or his employees, clients, and partners. After all, a man with a dream can really change the world.
You can follow me on Twitter and LinkedIn!